SPEECH THERAPY CENTER
 SPEECH THERAPY:
SPEECH THERAPY:
Speech therapy, or speech-language therapy, is a specialized form of therapy that focuses on improving communication abilities, including speech, language, cognitive-communication, and swallowing disorders. What makes speech therapy unique is the wide range of issues it addresses and the tailored, individualized approaches used to meet each patient’s specific needs. Here are key elements that make speech therapy unique:
1. Diverse Range of Disorders Treated
- Speech Disorders: These include problems with articulation (how speech sounds are made), fluency (e.g., stuttering), and voice (e.g., hoarseness or voice disorders).
- Language Disorders: These involve difficulty understanding language (receptive language) or using language to communicate (expressive language). Language disorders can impact both children and adults.
- Cognitive-Communication Disorders: This includes difficulties with attention, memory, problem-solving, and executive function, often seen after brain injuries or in conditions like dementia.
- Swallowing Disorders (Dysphagia): Speech therapists also help with feeding and swallowing difficulties, which can arise from neurological issues, surgery, or developmental delays.
2. Customized, Patient-Centered Approach
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Speech therapists design customized plans based on the specific needs, age, and abilities of each patient. For example, therapy for a child with autism will be different from therapy for an adult recovering from a stroke.
- Goal-Oriented Therapy: The therapist works closely with the patient and their family to set achievable, realistic goals that may focus on anything from improving social communication to restoring swallowing function.
3. Wide Range of Ages and Conditions
- Early Intervention for Children: Speech therapy is commonly used for children with developmental delays, speech or language disorders, or conditions like autism or Down syndrome. Early intervention can greatly improve outcomes for children with communication challenges.
- Adult Therapy: Speech therapy is also essential for adults, especially those who have suffered from strokes, traumatic brain injuries, or neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s. Adults may need help regaining speech, improving clarity, or recovering language skills.
4. Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC)
- Use of Assistive Technology: For individuals who are non-verbal or have severe communication difficulties, speech therapists incorporate AAC devices, including communication boards, speech-generating devices, and tablet apps, to help the patient express themselves.
- Personalized AAC Systems: These tools are customized to the individual’s physical and cognitive abilities, allowing even those with significant impairments to communicate.
5. Emphasis on Both Receptive and Expressive Language
- Understanding Language (Receptive): Therapy often focuses on improving the ability to understand and process language. This is crucial for patients with conditions like aphasia or cognitive decline.
- Producing Language (Expressive): Therapy also targets the ability to express thoughts and ideas through words, gestures, or writing. For example, a patient with aphasia may need to relearn how to find words, form sentences, or communicate in new ways.
6. Multisensory and Interactive Techniques
- Play-Based Therapy for Children: To engage children, speech therapists often use play-based approaches, incorporating toys, games, songs, and stories. These strategies make learning fun and less intimidating.
- Interactive and Functional Practice for Adults: For adults, therapy may focus on practical and functional communication exercises, like having conversations, ordering food, or discussing daily routines, using role-playing and real-life scenarios.
7. Rehabilitation for Neurological Conditions
- Aphasia Therapy (After Stroke or Brain Injury): For people with aphasia, speech therapy focuses on helping them relearn language skills or find alternative ways to communicate, such as using gestures, drawing, or AAC devices.
- Voice and Swallowing Therapy (e.g., Parkinson’s Disease): Patients with Parkinson’s disease or other neurological conditions may require therapy to strengthen muscles involved in speech and swallowing or to improve vocal loudness and clarity (as seen in treatments like the Lee Silverman Voice Treatment, or LSVT).
8. Swallowing and Feeding Therapy
- Dysphagia Management: For patients with dysphagia, speech therapists work on exercises to improve the strength and coordination of the muscles involved in swallowing. This is particularly important for patients who are at risk of aspiration (food or liquids entering the lungs).
- Modified Diets and Techniques: Therapists also provide guidance on modified diets, thickened liquids, or safe swallowing techniques to prevent choking or aspiration.
9. Family and Caregiver Involvement
- Educating Families: Family involvement is critical in speech therapy. Therapists often provide parents or caregivers with strategies and exercises to reinforce at home, especially for children or patients with cognitive impairments.
- Home Programs: Ongoing practice at home, guided by family members or caregivers, can accelerate progress and improve the patient’s ability to apply new skills in everyday situations.
10. Holistic Communication Support
- Social Communication Skills: For patients with social communication difficulties (e.g., children with autism or adults with brain injuries), speech therapy helps improve skills like making eye contact, understanding nonverbal cues, taking turns in conversation, and understanding social rules.
- Emotional and Behavioral Support: Communication challenges can be emotionally frustrating. Speech therapists also address the emotional aspects of therapy, helping patients cope with the frustrations of communication difficulties and build confidence in their abilities.
11. Continual Adaptation and Monitoring
- Ongoing Assessment: Speech therapists continually assess progress and adapt therapy techniques as the patient improves or as new challenges arise. This ensures that therapy remains effective and responsive to the patient’s changing needs.
- Functional Outcome Focus: Ultimately, speech therapy aims to improve the patient’s ability to function in everyday life, whether that involves speaking, listening, writing, reading, or swallowing.
Speech therapy is unique because of its flexibility, focus on communication in all forms, and its use of cutting-edge technology and interactive methods to achieve the best outcomes for people of all ages and conditions
GYNAECOLOGY PHYSIOTHERAPY
If you’re searching for the best Gynaecological Physiotherapy Treatment in Dhaka, you should know we’ve treated hundreds of patients successfully with gynecological conditions ranging from:
Get Fast & Effective Physiotherapy Treatments
- Urinary Incontinence (Stress, Urge, Mixed)
- Dysmenorrhea/Pain During Menstruation
- Dyspareunia/Pain During Sexual Intercourse
- Post Menopausal symptom
- Post Surgical Condition (Breast & Uterus Surgery)
- Pelvic organ Prolapse (Uterine Prolapse)
- Pregnancy
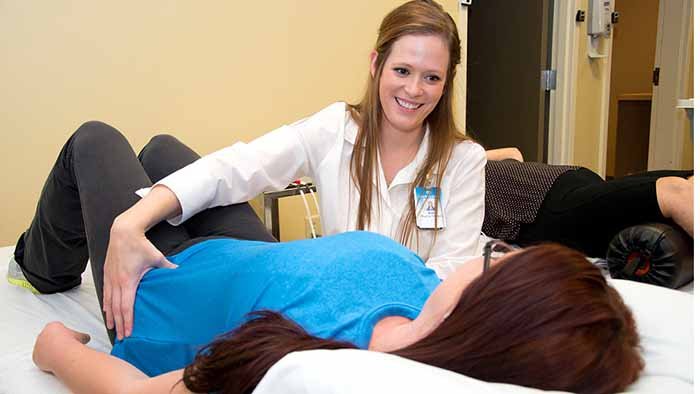

At Active Care BD, we offer life-changing physiotherapy specialties & techniques.
- We treat patient’s condition, not just the symptoms.
- We apply the most effective physical therapy techniques.
- We use latest physiotherapy equipment & technology.
- We work as a team to ensure you regain a better lifestyle.
- We ensure patients’ comfort, safety, privacy, and dignity.
BOOK YOUR CONSULTATION
Enter your details below and we will follow up with you to book your appointment.
SCHEDULE YOUR APPOINTMENT
Submit your info to confirm your appointment
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
Learn commonly asked questions about our physiotherapy services.
Active Care BD is enriched with advanced medical equipment and here the Physiotherapists are skilled with different manual techniques that help you in quick pain relief.
It depends on the severity of the condition. Most of the cases require 8-10 sessions.
You will be happy to know that there are no side effects of physiotherapy treatment.
